堆
堆必须是一个完全二叉树。除了最后一层,其他层的节点个数都是满的,最后一层的节点都靠左排列
堆中的每个节点的值必须大于等于(或者小于等于)其子树中每个节点的值或者说堆中每个节点的值都大于等于(或者小于等于)其左右子节点的值。这两种表述是等价的。
对于每个节点的值都大于等于子树中每个节点值的堆,我们叫作“大顶堆”。对于每个节点的值都小于等于子树中每个节点值的堆,我们叫作“小顶堆”。

在图中1和2是大顶堆,3是小顶堆,4不是堆(最后一层不是右子节点)。
实现
完全二叉树比较适合用数组来存储。用数组来存储完全二叉树是非常节省存储空间的。因为我们不需要存储左右子节点的指针,单纯地通过数组的下标,就可以找到一个节点的左右子节点和父节点。

数组中下标为 i 的节点的左子节点,就是下标为 $i$的节点,右子节点就是下标为$i*2+1$的节点,父节点就是下标为 $$\frac{i}{2}$$的节点。
堆化
新插入的元素放到堆的最后,我们需要进行调整,让其重新满足堆的特性,这个过程就叫作堆化(heapify)。 堆化实际上有两种,从下往上和从上往下。

新插入的节点与父节点对比大小。如果不满足子节点小于等于父节点的大小关系,就互换两个节点。重复这个过程,直到父子节点之间满足刚说的那种大小关系。

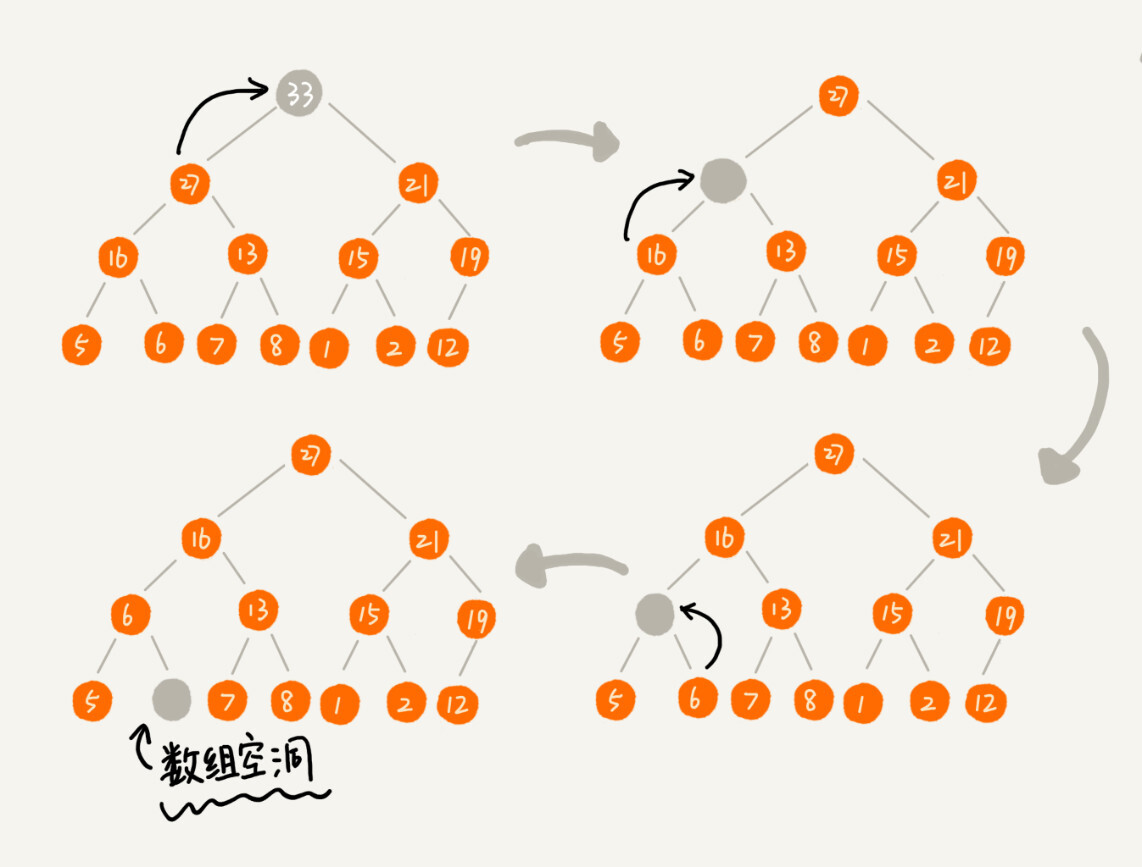
删除堆顶元素
堆顶元素存储的其实是堆中数据中的最大值或者最小值。 如果我们构造的是大顶堆,堆顶元素就是最大的元素。当我们删除堆顶元素之后,就需要把第二大的元素放到堆顶,那第二大元素肯定会出现在左右子节点中。然后我们再迭代地删除第二大节点,以此类推,直到叶子节点被删除。
代码
复用原先的Array代码并且加以改造
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
public Array(E[] arr){
data = (E[])new Object[arr.length];
for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i ++)
data[i] = arr[i];
size = arr.length;
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
public void swap(int i, int j){
if(i < 0 || i >= size || j < 0 || j >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Index is illegal.");
E t = data[i];
data[i] = data[j];
data[j] = t;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}public class MaxHeap<E extends Comparable<E>> {
private Array<E> data;
public MaxHeap(int capacity){
data = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public MaxHeap(){
data = new Array<>();
}
public MaxHeap(E[] arr){
data = new Array<>(arr);
for(int i = parent(arr.length - 1) ; i >= 0 ; i --)
siftDown(i);
}
// 返回堆中的元素个数
public int size(){
return data.getSize();
}
// 返回一个布尔值, 表示堆中是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return data.isEmpty();
}
// 返回完全二叉树的数组表示中,一个索引所表示的元素的父亲节点的索引
private int parent(int index){
if(index == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index-0 doesn't have parent.");
return (index - 1) / 2;
}
// 返回完全二叉树的数组表示中,一个索引所表示的元素的左孩子节点的索引
private int leftChild(int index){
return index * 2 + 1;
}
// 返回完全二叉树的数组表示中,一个索引所表示的元素的右孩子节点的索引
private int rightChild(int index){
return index * 2 + 2;
}
// 向堆中添加元素
public void add(E e){
data.addLast(e);
siftUp(data.getSize() - 1);
}
private void siftUp(int k){
while(k > 0 && data.get(parent(k)).compareTo(data.get(k)) < 0 ){
data.swap(k, parent(k));
k = parent(k);
}
}
// 看堆中的最大元素
public E findMax(){
if(data.getSize() == 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can not findMax when heap is empty.");
return data.get(0);
}
// 取出堆中最大元素
public E extractMax(){
E ret = findMax();
data.swap(0, data.getSize() - 1);
data.removeLast();
siftDown(0);
return ret;
}
private void siftDown(int k){
while(leftChild(k) < data.getSize()){
int j = leftChild(k); // 在此轮循环中,data[k]和data[j]交换位置
if( j + 1 < data.getSize() &&
data.get(j + 1).compareTo(data.get(j)) > 0 )
j ++;
// data[j] 是 leftChild 和 rightChild 中的最大值
if(data.get(k).compareTo(data.get(j)) >= 0 )
break;
data.swap(k, j);
k = j;
}
}
// 取出堆中的最大元素,并且替换成元素e
public E replace(E e){
E ret = findMax();
data.set(0, e);
siftDown(0);
return ret;
}
}import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
private static double testHeap(Integer[] testData, boolean isHeapify){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
MaxHeap<Integer> maxHeap;
if(isHeapify)
maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>(testData);
else{
maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>();
for(int num: testData)
maxHeap.add(num);
}
int[] arr = new int[testData.length];
for(int i = 0 ; i < testData.length ; i ++)
arr[i] = maxHeap.extractMax();
for(int i = 1 ; i < testData.length ; i ++)
if(arr[i-1] < arr[i])
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Error");
System.out.println("Test MaxHeap completed.");
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 1000000;
Random random = new Random();
Integer[] testData = new Integer[n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++)
testData[i] = random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
double time1 = testHeap(testData, false);
System.out.println("Without heapify: " + time1 + " s");
double time2 = testHeap(testData, true);
System.out.println("With heapify: " + time2 + " s");
}
}

优先队列
普通的队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,元素在队列尾追加,而从队列头删除。在优先队列中,元素被赋予优先级。当访问元素时,具有最高优先级的元素最先删除。优先队列具有最高级先出 (first in, largest out)的行为特征。通常采用堆数据结构来实现。
public class PriorityQueue<E extends Comparable<E>> implements Queue<E> {
private MaxHeap<E> maxHeap;
public PriorityQueue(){
maxHeap = new MaxHeap<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return maxHeap.size();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return maxHeap.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
return maxHeap.findMax();
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
maxHeap.add(e);
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
return maxHeap.extractMax();
}import java.util.Random;
public class PriorityQueueMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
Random random = new Random();
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
int size = 1000000;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
priorityQueue.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
if (i % 3 == 0)
priorityQueue.dequeue();
}
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
System.out.println("The priorityQueue size is :" + size +""+"\n After operation size is "+priorityQueue.getSize()+ "\n operation time is " + (((endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0)) + "s");
}
}

参考资料
《大话数据结构》
《数据结构与算法之美》
《玩转数据结构》

